The article DOI – what is it and how can I find it? Instruction
- May 12, 2023
- Posted by: Yury Subachev, PhD
- Categories: Classifiers, For young scientists
-
Post Views: 909
Many academics nowadays attach great importance to the DOI code. In recent years, it has become customary to specify the DOI in scientific reports and in forming a list of one’s publications. Nevertheless, not everyone understands the meaning and the essence of this abbreviation and asks a question: “The DOI of an article – what does it mean and how can I get it?
The acronym DOI stands for Digital Object Identifier which represents a global standard for displaying data about an object on the Internet.
But why do some articles have this code and others do not? What does it depend on? How does it influence the articles’ scientometric indicators? And how, if you have an article indexed with DOI in your local journal, can you get into the international database Scopus or Web of Science? You will learn all this from this article.
So, what is the article DOI? As previously mentioned, DOI means a unique standardised digital code that is assigned to materials posted in the Internet. The DOI code looks like a unique string of numbers, sometimes supplemented with letters.
The DOI code structure is divided into two parts: the prefix and the suffix. These parts are recorded consecutively with the “/” sign. Each has a special purpose and is structured in a specific way.

The first part is defined by the DOI corporation. The prefix refers to the publisher. It is issued by a registration agency. For this purpose, the publisher signs a contract with an agency and pays a registration fee. If the publisher changes the form of ownership its DOI will remain unchanged since the prefix identifies the publisher as such and not the journal owner.
As for the suffix, it is a label assigned by the publisher to the article. It is unique together with the prefix. It should be noted that each publisher has its own way to draw up the suffix.
2. What are the properties and functions of the DOI code?
The digital identifier helps to present information about documents in a compact manner. In addition, it simplifies the search of sought material within a huge array of publications contained in the web. This is because the DOI is actually a link to a permanent depository where the document is kept or to a page with its description. This link helps to find a sought object, even if the original posting site underwent changes.
The following information can usually be obtained based on the DOI:
- location of the document (URL);
- its full name;
- other identifiers: ISBN (for e-book), ISSN (for a journal);
- number of pages, issue number and volume, year of publication, etc.
What particular objects can be coded with the DOI?
Amazingly, almost any materials, not just academic articles!
This code can be assigned to almost any digital objects/resources. These include books, journals, scientific presentations, theses and just anything imaginable. Even separate parts of publications – drawings, tables, charts – may have such a code. This is convenient when some work was created by a team of authors.
3. In what way do we enter the DOI code when citing articles?
When citing articles in your research papers, be sure to include the DOI code – this will facilitate your readers’ search of information they need. Some international journals have introduced the practice of mandatory specification of the DOI code (if available) when citing articles.
The DOI identifier appears immediately after the bibliographic reference in the following form:
https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406211425758
or in a shorter form:
DOI: 10.1177/0954406211425758
4. Who has the right to assign DOI codes to scientific materials?
The DOI index has been assigned to electronic materials since 2000. The standards for its use are set by the parent organisation – International DOI Foundation (IDF).

Codes to particular materials are issued by special registration agencies. Each individual agency deals with a particular type of object or document: audio materials, video files, Internet resources, etc.
The registration of scientific articles, monographs, conference proceedings and theses is the prerogative of the influential company CrossRef. CrossRef is a non-profit association of academic publishers with about 2,000 members, which aims to promote scholarly communication worldwide through developing a scientific infrastructure and facilitates retrieval and citation of scientific information on the Internet. CrossRef has a database of over 68 million articles and other scholarly materials (books, theses, scientific papers, etc.). Most fundamental and reputable academic journals actively interact with it, in the first place.

The full list of all editions having own DOI prefix can be found at: https://www.crossref.org/06members/50go-live.html
5. What is the process of assigning the DOI code to articles?
The identifier is assigned to a whole material or parts of it, chapters or even figures and tables. For the most part, first-rate well-known international journals automatically assign DOI to the texts that were included in their publication portfolio. Gradually, this publishing practice is being borrowed by the Russian publishing practice. This enables Russian scientists to actively interact with the international journals and individual researchers.
For a publisher to be entitled to assign DOI codes to its materials, it applies to a registration agency, pays for the service, registers and receives a DOI prefix; subsequently it forms suffixes and assigns a full DOI ID to its online publications. The cost of such service for a journal is about $1-2 per one DOI, or about $200-400 if it pays for unlimited annual service.
At the same time, it should be understood that a journal can issue articles in any format – with or without the DOI. However, if a publication does not have a DOI it may end in being “lost” in the web, which will naturally have a negative impact on the citation rate of the paper. If the presence of this identifier is a critical issue for you as a scientist, then check with the journal’s editorial board before submitting your paper for publication. Remember that not every publisher can issue the DOI, but only those that have concluded an agreement with the official registrar.
However, you should be aware that the mere presence of the DOI code is in no way indicative of high quality of a publication or the proper level of a journal. It is just a criterion, when searching for an object in the ocean of digital data.
6. How can I find out whether the article has been assigned the DOI code?
The DOI code can be found directly in the text of the article/material; at the same time, there are no uniform rules as to where it can and can not be placed. Thus, it can be found anywhere in the article, even in a footnote.
The DOI may also appear on the journal’s or publisher’s website, in the description of a publication.
7. How can I find or download an article using the DOI?
Owing to the DOI, it is easy to find a sought article on your own, in particular, on the International DOI Foundation website http://www.doi.org/ or Crossref website crossref.org.
1. Search through the International DOI Foundation. At http://www.doi.org/, enter the code in the appropriate search box and click Submit:
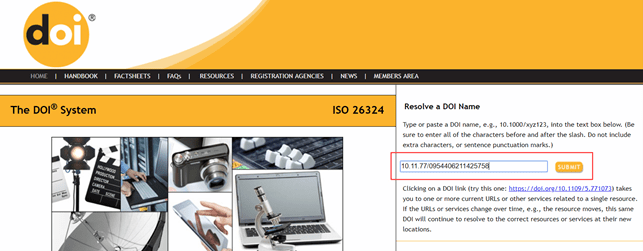
and here is the publication page on the publisher’s website with all its details:

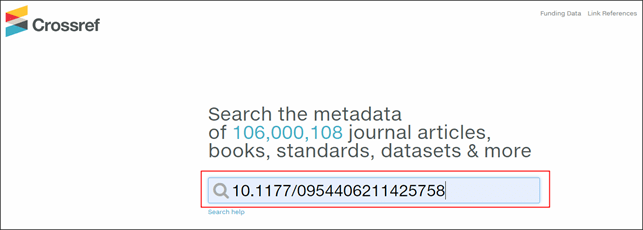
2. Search through the Crossref. At https://search.crossref.org/, enter the code in the search box in the same way:
and get all the information from the Crossref database, including the article volume, number and pages, as published in the journal:
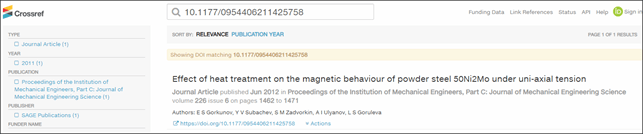
The publisher itself decides on accessibility of an article. If an article is in the public domain it will be available for downloading, and if it is in the private domain then only its abstract and brief description will be visible. It can be further searched in full-text scientific article databases which can be accessed at the library of a research organisation or a university having a due subscription.
It is also important that the DOI can always be used to find information about an article even if the publisher is no longer operating or its website is unavailable.
8. Are the DOI-coded articles automatically included in the Scopus and Web of Science databases?
Important: If an article has a DOI this does not mean that it will automatically be included in the international scientific citation indexes Scopus and Web of Science.
The inclusion of journals in the Scopus and Web of Science databases and getting DOI are the things independent of each other. But one interesting point is notable: if a publication with DOI is referenced by the author of an article that was published in a journal from the Scopus or Web of Science database, then this publication is also included in the relevant citation database even if it was published in an undistinguished local journal. However, it is important to know that such a publication will not be entered in the Scopus or Web of Science system as a full-value indexed publication; therefore this publication should not be referred to as indexed in the database – it will only have a source status, but will not appear in the database.
Nevertheless, after a DOI is assigned to an article, an abstract is created for it in the English language and posted on doi.org. Thus even a Chinese, Spanish, Bulgarian article (or written in any other non-English language) becomes visible to scholars all over the world. It, in turn, is indexed by search engines and becomes publicly accessible.
9. What are the benefits of DOI-coded articles?
It is important for the authors of scientific publications that the DOI system guarantees unambiguous identification of digital objects in its information environment, as well as metadata consistency, their disclosure and compatibility.
If your articles come with a DOI identifier you, as an author, get a number of benefits:
- a permanent, unique index assigned to each published article and its secure online storage;
- increased reach and citation rate of the publication;
- your increased visibility and popularity as an author;
- a possibility of being cited by other authors and inclusion of a DOI-coded article in the international databases Web of Science, Scopus and others.
Owing to the DOI code, one can quickly find a sought article on the Internet and see all of its imprint data at once. This kind of search yields much better results than just searching for an article by its title through a conventional search engine or citation databases. This approach often produces irrelevant information. Therefore, researchers plunge into the Klondike of databases on their subject area and search for relevant material in them, including with the help of the DOI.
The DOI also plays a significant role in scientometrics. The thing is that presently it must be entered when compiling scientific reports, completing profiles in information systems that help to assess the performance of scientific institutions.
When rewriting or copying all imprint data of a publication – its title, authors, journal title, publisher, issue and page number – it is possible to make an error. In this case, regretfully, the search systems will not find the sought article. Meanwhile the DOI reduces the probability of error and its subsequent reproduction.
In addition, the DOI is designated for convenience of subsequent citation and indexing of articles.
Conclusion
We have covered a number of DOI-related questions in detail as much as possible, expounding what the DOI is; and most importantly, we have answered the question “The DOI-indexed article – how can I find it?”. Below are two links that will allow you to find information about an electronic object as based on a DOI code:
Although the DOI ID is not necessary for publication it will still help indirectly to increase the citation of scholarly materials in the world indexes – for this purpose, articles should be placed in the journals that assign DOI to your work automatically. All articles in the global information databases, such as WoS or Scopus, are provided with a DOI code – this is a prerequisite for posting materials in them. However, one can observe that not all local journals so far provide articles with this identifier.
The DOI helps to find all information about a publication quickly and easily, to cite an article in a convenient and concise manner and to store the information about scientific papers in the Internet on a secure basis.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 2
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
